What is Osteoarthritis ?
Osteoarthritis is the most common problem among arthritis , millions of old age people suffers frequently.
It is a very common type of arthritis people get affected.
Definition of Osteoarthritis
This is a disease related to joints of the bones in various locations of the body.Arthritis including pain, swelling around the joints, stiffness or reddish discomfort occurs very often in people facing osteoarthritis.
What are the causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can damage all the areas in and around of the joint
- Cartilage
- Tendons and ligaments.
- Synovium
- Bone
- Meniscus in the knee
Damage to the soft tissues in the joint leads to pain, swelling, and loss of joint motion. The involved joint over time lose its normal activity and movement restrictions sets in. Also, small bone growths called as osteophytes which are nothing but bone spurs starts to grow on the edges of the arthritic joint.
Osteoarthritis Risk Factors
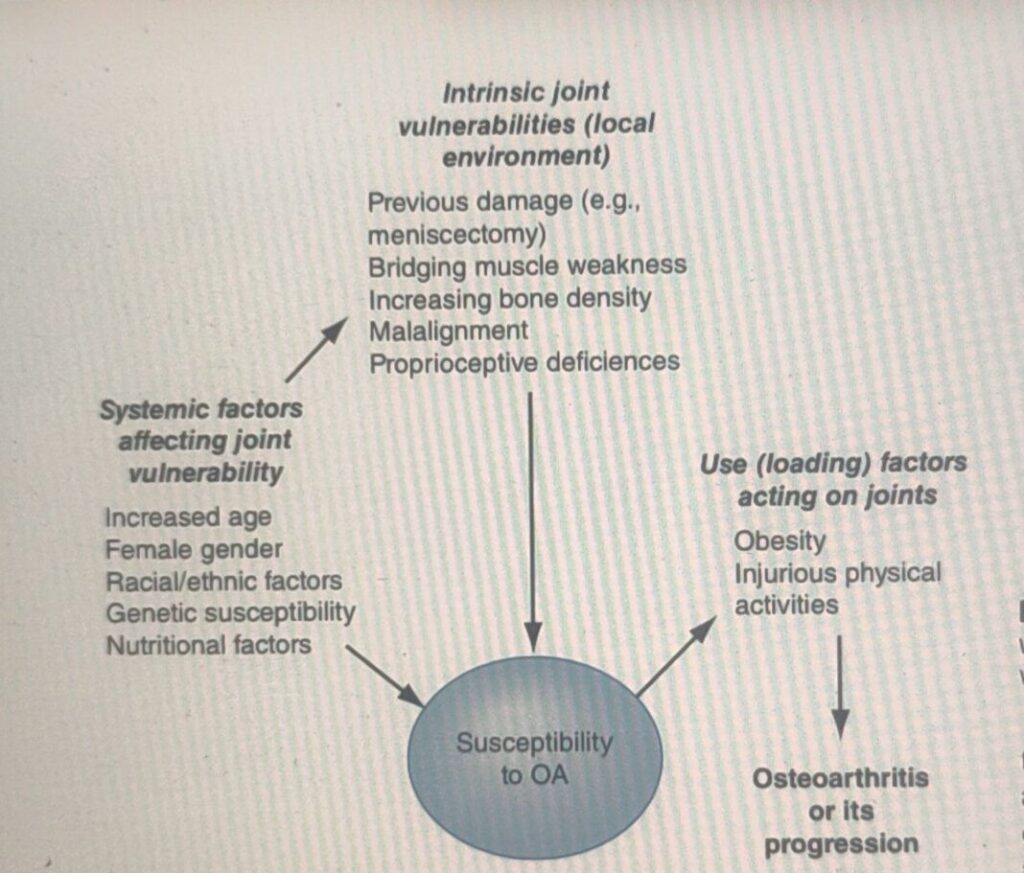
Mechanism of Osteoarthritis Development
Usually our joint contains Synovial fluids. It helps in reducing friction between articulating cartilage surfaces. Particles like Hyaluronic Acid and Lubricin helps to maintain the functioning. Synovial inflammation or injuries decrease the concentration leading to friction induced joint wear. This mechanism helps in development of Osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis epidemiology and age Involvement
Few decades ago, osteoarthritis was a problem of aged people over 50-55 but nowadays it has begun a major problem among late adults – aged over 30 to 40.A Juvenile form of this disease is seen among younger children of five to fifteen years denoted as Rheumatoid Arthritis affecting mainly cardiac valves forming vegetative nodules and damaging valve cusps.
Arthritis vs Osteoarthritis
Arthritis is a broader heading under which comes two form of disease.
One of the form is a kind of inflammatory arthritis whuch includes – Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythromatosis and Ankylosing Spondylitis.
And the second one is a kind of arthritis related to bones – osteoarthritis.
People should not neglect the suffering of bone pain around knee joint, shoulder or pelvic bones, infact of toes. As it will aggreviate the arthritic condition.If younger people post sore-throat or upper respiratory infections feels migratory pain around joints, immediately contact physian as it is a sign of developing – Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Osteoarthritis sign and symptoms
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Tenderness
- Loss of flexibility
- Grating sensation
- Bone spurs
- Swelling
Osteoarthritis affected joints
Osteoarthritis commonly affects joints of Hand usually first metatarsal phalangeal joint , Knee, Hip, Cervical and Lumbosacral joint.
Osteoarthritis Knee
Osteoarthritis of the knee is more common in “women” than in males. “Some other factors contributing to the condition of the knee include advanced age, being over weight or obese, previous knee injuries or surgery, and certain jobs that require constant knee stress-bending .
Osteoarthritis Hand Joint
They usually affects Distal and Proximal Inter Phalangeal Joints.
Osteoarthritis of Hip
In Osteoarthritis of hip, Pain and Stiffness in the hip joint will occur. Also pain can be in the groin, inner thigh, or buttocks. Sometimes, the pain from arthritis in the hip can spread to the knees.
Osteoarthritis of Spine
There might be stiffness and pain in the neck or lower back
Some features patients experience in Osteoarthritis
- Morning sickness of excruciating pain around joints.
- Limbs not working properly when they wake up
- Swelling around their mouth opening
- Rashes over face due to sunlight accompanied by hair loss
- Dryness of mouth as well as eyes
- Immense backache, especially at night
- Women are specially affected by arthritis more
- Problem in walking or standing after sitting for a longer time
Osteoarthritis Diagnosis & Treatment
1. Stop using painkillers randomly according to your own to treat arthritis
2.Immediately talk to a physician and you have to remember each arthritic condition has different treatment protocol
3. This is a reversible disease, so create awareness, people can be cured if treatment is followed correctly.
Importance of blood test for Osteoarthritis Patients
There’s no blood test for detecting osteoarthritis directly.
Diagnosing osteoarthritis (OA) is based largely on symptoms and a physical exam.Blood test is done to rule out rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
Tests to be done are
- Antinuclear antibody
- Rheumatoid factor
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
- Uric acid
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
Home (Physical) Management of Osteoarthritis
- Avoid painful activities
- Unloading joint by redistribution of load
- Improvement of muscles strength
- Physiotherapy
- Weight loss
Osteoarthritis Medications or Medicines
Analgesics in Osteoarthritis
They relieves pain.They include acetaminophen and opioids like agents. Acetaminophen is available over the counter (OTC); opioids must be prescribed by a doctor.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
These are the most commonly used drugs.They help patient to to get relief from inflammation and pain. They include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen and celecoxib.These drugs are available either OTC or by prescription. The OTC versions only help to get relief from pain but not inflammation.
Corticosteroids in Osteoarthritis
These anti-inflammatory medicines work in a similar way to a hormone called cortisol. The medicine is taken by mouth or injected into the joint at a doctor’s office.They are strictly used upon physician’s prescription.
Best medication for osteoarthritis
Most popular drugs to treat osteoarthritic pain is NSAID.
Best methods for pain relief in osteoarthritis
Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs also known as NSAIDs are the most effective oral medicines for Osteoarthritis . NSAID includes ibuprofen, Naproxen and Diclofenac
Osteoarthritis future complications
Sleep disruption
Disruption of sleep due to Pain and joint stiffness is a common complication.
- Anxiety and depression
- Sleep disruption
- Reduced productivity
- Weight gain
- Stress fractures
Best supplements for Osteoarthritis Patients
Difference between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Arthroscopy as Treatment in Osteoarthritis
In advanced stages of osteoarthritis (OA), knee replacement is a common intervention.
Early conservative approaches involve weight management, exercise, physical therapy, and the use of pain medications like corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid injections.
If symptoms persist and increases , surgeons may consider arthroscopic knee surgery as an additional option.
As arthritis causes knee pain, arthroscopic knee surgery isn’t always an effective treatment for osteoarthritis.There is also a relatively long recovery time (two to six weeks) and also a limited mobility after surgery
A possible exception to this recommendation is for patients who have a fully locked knee and aren’t able to completely straighten the knee joint. In arthritis with associated meniscal tears or loose bone or cartilage fragments, arthroscopic surgery can give good benefits.